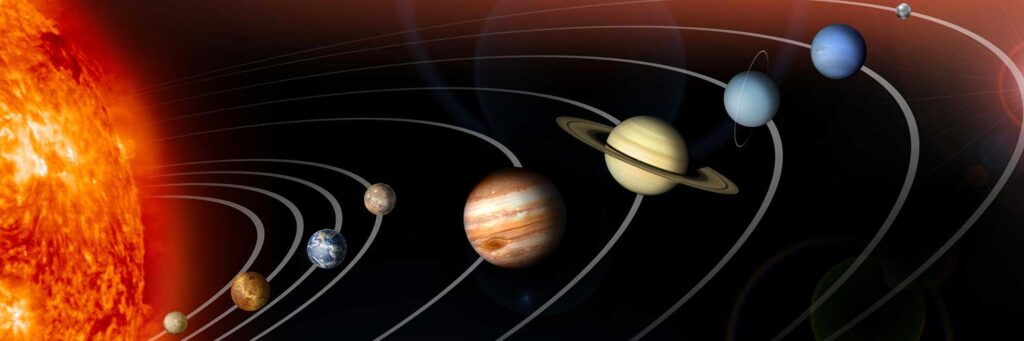
The solar system is a collection of celestial bodies, including the Sun, planets, moons, asteroids, comets, and other objects, that are bound together by gravity. The Sun, a star at the center of the solar system, provides light and energy to the planets and other objects orbiting it. Here’s an overview of the key components of the solar system:
1. The Sun:
- The Sun is a massive star that is the center of the solar system. It is made up primarily of hydrogen and helium and produces energy through nuclear fusion. The Sun’s gravity keeps all the objects in the solar system in orbit around it.
2. Planets:
There are eight planets in the solar system, which orbit the Sun in elliptical paths. The planets are divided into two categories: terrestrial (rocky) planets and gas giants.
- Terrestrial Planets (Rocky Planets):
- Mercury: The closest planet to the Sun, with extreme temperature variations.
- Venus: Similar in size to Earth, but with a thick, toxic atmosphere and surface temperatures hot enough to melt lead.
- Earth: The only known planet with life, Earth has a breathable atmosphere and liquid water on its surface.
- Mars: Known as the Red Planet, Mars has a thin atmosphere and features like mountains, valleys, and polar ice caps.
- Gas Giants (Jovian Planets):
- Jupiter: The largest planet in the solar system, Jupiter has a strong magnetic field and is known for its Great Red Spot, a massive storm.
- Saturn: Known for its stunning ring system, Saturn is the second-largest planet and is made mostly of hydrogen and helium.
- Uranus: A gas giant with a blue-green color due to methane in its atmosphere, Uranus has a unique sideways rotation.
- Neptune: The farthest planet from the Sun, Neptune is a cold, blue planet with strong winds and storms.
3. Dwarf Planets:
In addition to the eight main planets, there are also dwarf planets, which are similar to planets but do not dominate their orbits. The most famous dwarf planet is Pluto, which was once considered the ninth planet.
4. Moons:
Many planets in the solar system have natural satellites, or moons, that orbit them. For example:
- Earth has one moon.
- Jupiter has over 70 moons, including Ganymede, the largest moon in the solar system.
- Saturn has more than 80 moons, with Titan being the largest.
5. Asteroids and the Asteroid Belt:
- The Asteroid Belt is a region between Mars and Jupiter that contains a large number of rocky objects called asteroids.
- Asteroids are small, rocky bodies that orbit the Sun. Some are large, like Ceres, while others are small and irregular in shape.
6. Comets:
- Comets are icy bodies that originate in the outer regions of the solar system. They are made of dust, rock, and frozen gases.
- When comets approach the Sun, the heat causes their icy nucleus to vaporize, creating a glowing coma and a visible tail that points away from the Sun.
7. Kuiper Belt and Oort Cloud:
- The Kuiper Belt is a region beyond Neptune that contains many icy objects, including dwarf planets like Pluto.
- The Oort Cloud is a theoretical distant region, far beyond the Kuiper Belt, thought to contain icy bodies that could become comets.
Structure of the Solar System:
- Inner Solar System: Includes the Sun, the four terrestrial planets (Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars), and their moons.
- Outer Solar System: Includes the gas giants (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune), their moons, and the asteroid belt.
- Beyond the Solar System: The Kuiper Belt, Oort Cloud, and other distant regions.
Summary:
- The Sun is the central source of energy.
- Eight planets orbit the Sun, categorized as terrestrial or gas giants.
- Moons, asteroids, comets, and dwarf planets are also part of the solar system.
- The solar system is vast and includes various objects, each with unique features and characteristics.

Leave a Reply