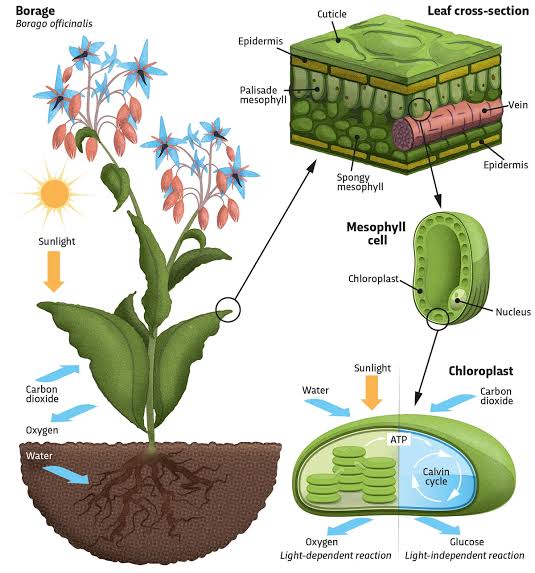
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy, typically from the Sun, into chemical energy stored in glucose (a type of sugar). This process is essential for life on Earth as it provides the primary energy source for nearly all ecosystems and produces oxygen, which is vital for the survival of many organisms, including humans.
The Process of Photosynthesis:
Photosynthesis occurs mainly in the chloroplasts of plant cells, particularly in the leaves, and involves two main stages: the light-dependent reactions and the light-independent reactions (also known as the Calvin Cycle).
1. Light-Dependent Reactions:
These reactions occur in the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplasts and require light to take place.
- Absorption of Light: Chlorophyll, the green pigment in plants, absorbs sunlight. The energy from this light is used to excite electrons in the chlorophyll molecules.
- Water Splitting: The excited electrons are passed through a series of proteins known as the electron transport chain. This process also splits water molecules (H₂O) into oxygen (O₂), protons (hydrogen ions, H⁺), and electrons. The oxygen is released as a byproduct.
- ATP and NADPH Formation: The energy from the electrons is used to convert ADP (adenosine diphosphate) into ATP (adenosine triphosphate), and to reduce NADP+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate) to NADPH (the reduced form). Both ATP and NADPH are energy carriers used in the next stage of photosynthesis.
2. Light-Independent Reactions (Calvin Cycle):
These reactions occur in the stroma of the chloroplasts and do not require light directly, but they depend on the ATP and NADPH produced in the light-dependent reactions.
- Carbon Fixation: The enzyme RuBisCO helps convert carbon dioxide (CO₂) from the atmosphere into a 5-carbon molecule called ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP).
- Formation of Glucose: Through a series of enzyme-driven reactions, the carbon atoms from CO₂ are incorporated into a sugar molecule (glucose, C₆H₁₂O₆). This process uses the ATP and NADPH from the light-dependent reactions to power the production of glucose.
The Overall Chemical Equation for Photosynthesis:
The general equation for photosynthesis is: 6CO2+6H2O+light energy→C6H12O6+6O26CO_2 + 6H_2O + \text{light energy} \rightarrow C_6H_{12}O_6 + 6O_2
- 6 molecules of carbon dioxide (CO₂) + 6 molecules of water (H₂O) + light energy produce 1 molecule of glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆) and 6 molecules of oxygen (O₂).
Importance of Photosynthesis:
- Energy Production: Photosynthesis is the primary source of energy for almost all life on Earth. Plants, algae, and some bacteria use the energy from photosynthesis to grow, reproduce, and carry out their life functions. Animals, including humans, depend on these organisms for food, which in turn provides energy through cellular respiration.
- Oxygen Production: Photosynthesis is the process by which plants release oxygen into the atmosphere as a byproduct. This oxygen is essential for the survival of aerobic organisms (those that need oxygen for respiration), including humans.
- Carbon Dioxide Reduction: Photosynthesis also helps regulate the levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, which is important for controlling the Earth’s climate.
Summary:
- Photosynthesis is the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy, storing it in the form of glucose.
- It involves two stages: the light-dependent reactions, which capture energy from sunlight, and the light-independent reactions (Calvin Cycle), which use that energy to convert carbon dioxide into glucose.
- The process produces oxygen and helps sustain life on Earth by providing energy and maintaining atmospheric balance.

Leave a Reply