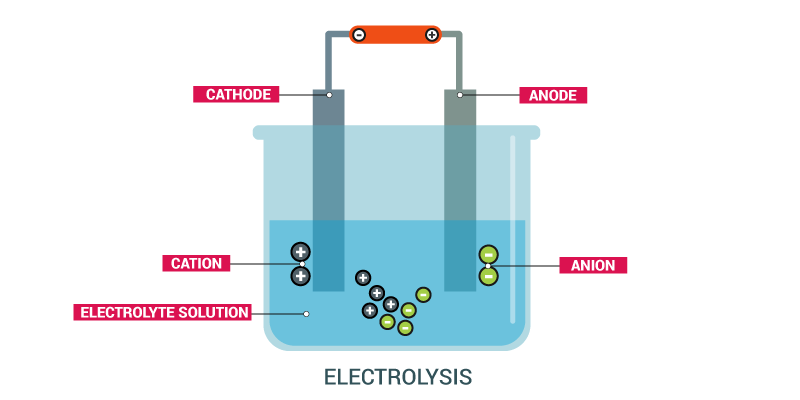
Electrolysis of water
Electrolysis of water is the process of converting water (H2O) into hydrogen (H+) and hydroxide (OH-) ions by passing an electric current through it. Ions move to the opposing electrodes, releasing pure hydrogen (H2) and oxygen (O2) gases. Electrolysis of water is an oxidation-reduction reaction that does not occur spontaneously. Since the heat in the form of electricity is supplied to the electrolytic cell in the electrolysis of water, the reaction is endothermic.
Apllications of Electrolysis
Nowadays the electrolytic process is widely used in various industrial applications. The major applications of the electrolysis are given below.
- Extraction of metal from their ores.
The electrolytic process is used for extracting out the pure metal from their ores, this process is known as electro-extraction. In the electro-extraction, the metal ore is treated with strong acid or is melted and then a DC current is passed through the resulting solution, the solution is decomposed and pure metal is deposited on the cathode.
- Refining of metals
electrolysis is also used for refining of metals and the process is termed as electro-refining. In electro-refining, the anode of impure metal is placed in a suitable electrolytic solution. When DC current is passed through the solution, pure metal is deposited on the cathode.
- Manufacturing of chemical
he electrolytic process is also used for manufacturing of various chemicals. When an electric current is passed through the solution of some compound, the compound gets breakdown into its constituent components which are liberated at the anode and cathode, which in turn can be collected.
- Electropolishing
the electropolishing is an electrolytic process that removes materials from a metallic workpiece. It is also known as electrochemical polishing or electrolytic polishing.
Process of electrolysis.
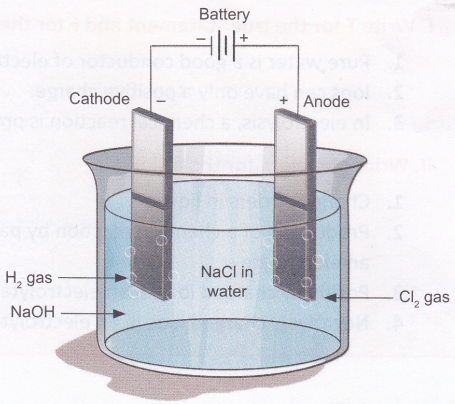
In the process of electrolysis, there is an interchange of ions and atoms due to the addition or removal of electrons from the external circuit. Basically, on passing current, cations move to the cathode, take electrons from the cathode (given by the supply source battery), and are discharged into the neutral atom. The neutral atom, if solid, is deposited on the cathode and, if gas, moves upwards. This is a reduction process, and the cation is reduced at the cathode.
The electrolysis process, while useful to get elemental forms from compounds directly, can also be used indirectly in the metallurgy of alkali and alkaline earth metals, purification of metals, deposition of metals, preparation of compounds
THIS

Leave a Reply