
An international mathematician is a professional in the field of mathematics who has made significant contributions to the discipline on a global scale. Some of these mathematicians are renowned for their work across various areas of mathematics, such as pure mathematics, applied mathematics, number theory, algebra, geometry, calculus, and many more. Here are a few notable international mathematicians who have made lasting impacts:

1. Srinivasa Ramanujan (1887–1920):
- An Indian mathematician with groundbreaking contributions to number theory, continued fractions, and infinite series.
- Despite limited formal training, his intuitive grasp of complex mathematical concepts earned him recognition worldwide, especially after his correspondence with G.H. Hardy.
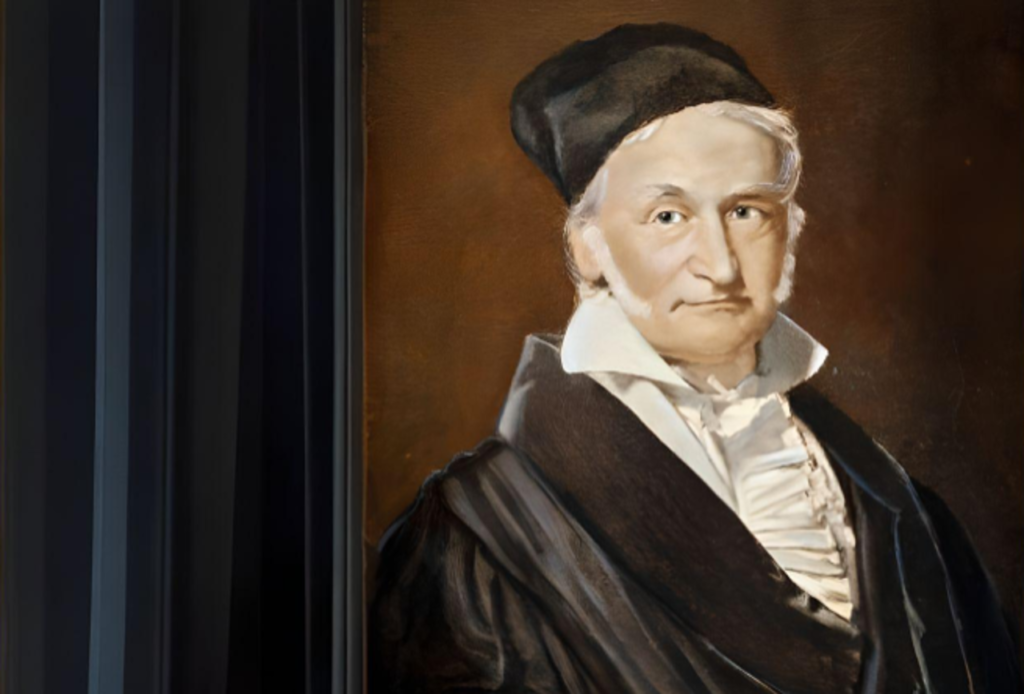

2.Carl Friedrich Gauss (1777–1855):
- Known as the “Prince of Mathematicians,” Gauss made contributions across many fields, including number theory, algebra, statistics, analysis, and astronomy.
- Famous works: The Gaussian distribution in statistics and Gauss’s Law in electromagnetism.
3. Pierre-Simon Laplace (1749–1827):
- A French mathematician and astronomer who worked on celestial mechanics, probability theory, and statistics.
- His work in probability theory, including the Laplace transform, is still widely used in engineering and applied mathematics.
4. Euclid (c. 300 BCE):
- Often called the “Father of Geometry,” Euclid was a Greek mathematician who wrote the famous treatise Elements, which has been used as a textbook for centuries and forms the basis for modern geometry.
5. Isaac Newton (1643–1727):
- An English mathematician and physicist, Newton co-founded calculus (independently of Leibniz) and made groundbreaking work in physics, laying the foundation for classical mechanics.
- His laws of motion and universal gravitation revolutionized science.
6. G.H. Hardy (1877–1947):
- A British mathematician known for his work in number theory and mathematical analysis.
- An Indian mathematician with groundbreaking contributions to number theory, continued fractions, and infinite series.
- Despite limited formal training, his intuitive grasp of complex mathematical concepts earned him recognition worldwide, especially after his correspondence with G.H. Hardy.
7. John von Neumann (1903–1957):
- A Hungarian-American mathematician and computer scientist who made foundational contributions to game theory, quantum mechanics, and computing.
- Known for the von Neumann architecture, which underlies most computer systems today.

8. Mary Cartwright (1900–1998):
- A British mathematician who worked on chaos theory and contributed to the development of nonlinear differential equations and systems.
- She was instrumental in the study of chaos theory and mathematical biology.
9. Emmy Noether (1882–1935):
- A German mathematician who revolutionized algebra and physics with Noether’s Theorem, which connects symmetries and conservation laws.
- She is considered one of the most influential women in mathematics.
10. Andrew Wiles (1953–present):
- A British mathematician who is best known for proving Fermat’s Last Theorem, a problem that had remained unsolved for over 350 years.
- His proof is one of the most significant achievements in modern mathematics.
11. Kurt Gödel (1906–1978):
- An Austrian-American logician and mathematician who is best known for his Incompleteness Theorems, which have profound implications for the foundations of mathematics.
- Gödel’s work demonstrated that no system of axioms can be both complete and consistent.
12. M. S. Raghunathan (1942–present):
- An Indian mathematician known for his contributions to the field of Lie groups and algebraic groups, as well as his work in number theory and geometry.
Summary:
These mathematicians are just a few examples of individuals who have contributed profoundly to the field of mathematics on an international scale. Their work has helped shape modern mathematics and continues to influence a wide variety of disciplines, including science, engineering, economics, and technology. Many of them have made advances that bridge the gap between theory and application, showcasing the universal importance of mathematics in understanding and solving real-world problems.

Leave a Reply